Each project is an opportunity for the company and each employee to grow — we gain experience, unique knowledge, and new emotions. In order to get more interesting projects, you need to be able to manage the result correctly. That is why different approaches to setting goals and evaluating results were invented.
If you are an IT manager, you know this firsthand. You are responsible for forming and achieving ambitious goals in a particularly volatile environment. In this context, the SMART approach comes to the rescue — a powerful tool that helps formulate goals so that they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
What is the SMART approach and how to correctly measure the progress of a project and an employee — we discuss in the article. We have collected tools that will help IT managers cope with the difficult task of managing achievements.
What is the SMART approach?
SMART is an abbreviation that consists of 5 aspects: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound. Let’s look at everything in more detail:
Specific
Let’s talk about goals. The first aspect is specificity. The goal must be clearly formulated. As a manager, you want to achieve something, but in order to soberly assess the situation, you need to step away from your thoughts, ambitions and set a clear task – to achieve a certain mark. In order to adequately evaluate the results of the department’s work later, you need to let employees understand what you expect from them.
Tip: Instead of “Increase sales”, use “Increase sales by 20% in the next quarter”.
So, if you set a goal “to increase sales”, at the end of a given period, if sales from the department increase by 1, the plan is fulfilled and employees are not responsible for the fact that you are not satisfied with the result.

Measurable
The goal must be measurable so that you can track progress. Specific metrics are used for this, which we will talk about later.
Tip: Measure sales growth through diverse metrics to see the big picture and the ability to analyze cause-and-effect relationships. Total sales, number of new customers, average order value, etc.
Achievable
The goal should be achievable and realistic. The metrics you choose should be based on the existing achievements and level of the company, the real situation on the market – and not your expectations.
If you give the team obviously unrealistic and unachievable indicators, even the most hard-working and motivated team will eventually lose momentum and there is a risk of losing valuable employees.
Tip: Make sure that increasing sales by 20% is possible in your niche and is not associated with overtime.
Relevant
The goal should be reasoned and consistent with the overall goals and strategies of the company. Metrics should reflect the existing structure of the company’s profits, not giving way to innovative proposals.
Example: If the strategic goal of the company is to expand into a new market, then the metrics can include the number of new regions, the number of new customers in these regions and market share.
Time-bound
Like tasks, goals should have deadlines. The most important thing is to set realistic deadlines, taking into account emergency situations and an adequate work rhythm.
Example: Achieve a 20% increase in sales over the next quarter.
How does the SMART approach relate to metrics?
Goal: Increase website traffic by 20% over the next year.
- Specific: The goal is specific — increase website traffic.
- Measurable: Use metrics such as number of unique visitors, number of page views.
- Achievable: Analyze current data and plan marketing campaigns to make sure the goal is achievable. Is there a source of new relevant visitors? Perhaps the lack of users is due to something else.
- Relevant: The goal is in line with the company’s overall strategy to increase its online presence and attract customers via the Internet. If the main sales channel is not the website and your services are not of interest to Internet users, is there any point in attracting an audience at all? Even if you attract a user, this does not mean that a sale or warm-up will occur.
- Time-bound: The goal has a specific time frame — 1 year.
How can metrics help an IT project manager?
- Identify a need or Decide
The SMART approach helps to clearly define goals and select relevant metrics to achieve them. Sometimes the team lacks certainty, it is unclear where to go – why sell, why create? And sometimes there are so many plans that it is easy to get lost in them. This is exactly why you need a tool that structures everything. Metrics provide clarity and direction for the team’s actions. - Tracking progress is useful not only for the manager, but also for the employee
With the help of measurable metrics, you can regularly track progress and make adjustments if necessary. - Motivation management
Achievable and time-bound goals motivate the team, as they see specific results of their efforts. - Making informed decisions
Relevant metrics provide data for analysis and decision-making based on actual results, not intuition and subjective experience. Employees will have no reason to dispute your decisions – the numbers will confirm your decision.
What is OKR?
OKR stands for Objectives and Key Results. OKR is a method of managing objectives and key results that helps organizations, teams, and individuals achieve ambitious goals by clearly defining and measuring specific results. This approach has been popularized by companies such as Intel and Google, and is used by many leading companies.
Objectives are ambitious, inspiring, and specific directions that an organization or team strives to achieve. They should be clear and meaningful in order to motivate and guide the team.
- Increase market share by 10%.
- Improve user experience on our website.
- Implement an innovative solution for automating business processes.
Key Results are specific, measurable indicators that determine whether the objectives have been successfully achieved. These results should be quantifiable and realistic.
- Attract 5,000 new customers.
- Increase repeat sales by 20%.
- Conduct 10 marketing campaigns reaching over 1 million people.
Using OKRs in IT projects helps teams and organizations clearly define goals and measurable results that lead to their achievement.
New Product Development
Objective: Develop and launch a new version of the mobile app
Key Result 1: Complete all major features by the end of the quarter.
Key Result 2: Conduct beta testing with 500 users and get feedback.
Key Result 3: Reduce the number of critical bugs to less than 5.
Key Result 4: Increase app performance by 30%.
DevOps
Objective: Improve infrastructure stability and reliability
Key Result 1: Increase uptime to 97.99%.
Key Result 2: Reduce mean time to repair (MTTR) after incidents to 30 minutes.
Key Result 3: Conduct and close all open incidents within the SLA (Service Level Agreement).
Key Result 4: Implement AI-based monitoring and alerting to predict failures.
What does KPI stand for?
KPIs are key performance indicators. These are metrics used to evaluate the success of an organization, team, project, or specific process in achieving its goals.
KPIs in IT are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively an IT department or project achieves its business goals. They can be related to system performance, service quality, user satisfaction, cost efficiency.

The Importance of KPIs in IT
How can you understand how effective your team or project is? One of the most reliable ways is to use key performance indicators, or KPIs. Have you ever wondered why some companies are more successful than others? The secret often lies in the ability to objectively evaluate performance. KPIs allow you to quantify results and efficiency, which helps you make informed and strategic decisions.
KPIs help you focus on the key elements that have the greatest impact on the success of your project or entire organization. This is especially true for companies with limited resources, when you need to know exactly where to direct your efforts.
In addition, using KPIs creates transparency in the work. You and your team know exactly what is required of you and can track your progress.
How can we not mention motivation? Clearly defined and achievable KPIs can significantly increase the fighting spirit of the team. When people know what they are striving for and what results are expected of them, it motivates them to work better.
Examples of KPIs in IT
System Performance
- Response Time – the average time it takes the system to process a request.
- System Uptime – the percentage of time the system is available and functioning.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) – the average time it takes to restore the system after a failure.
Development Quality
- Bugs per 1000 lines of code – a measure of code quality.
- Deployment Success Rate – the percentage of deployments that were completed without critical errors.
- Test Coverage – the percentage of code covered by automated tests.
Service Level
- Average Incident Resolution Time – the average time it takes to resolve a problem after it was discovered.
- Percentage of Incidents Resolved within SLA – the percentage of incidents resolved in accordance with the service level agreement.
User Satisfaction
- User Satisfaction Level – a rating obtained from user surveys.
- Number of User Complaints – the number of complaints received over a given period.
- Customer Intolerance – The percentage of customers who abandoned the service due to dissatisfaction.
Cost Efficiency
- ROI (Return on Investment) – The ratio of the profit received from investing in a project to the cost of implementing it.
- TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) – The total cost of owning and maintaining a system or product.
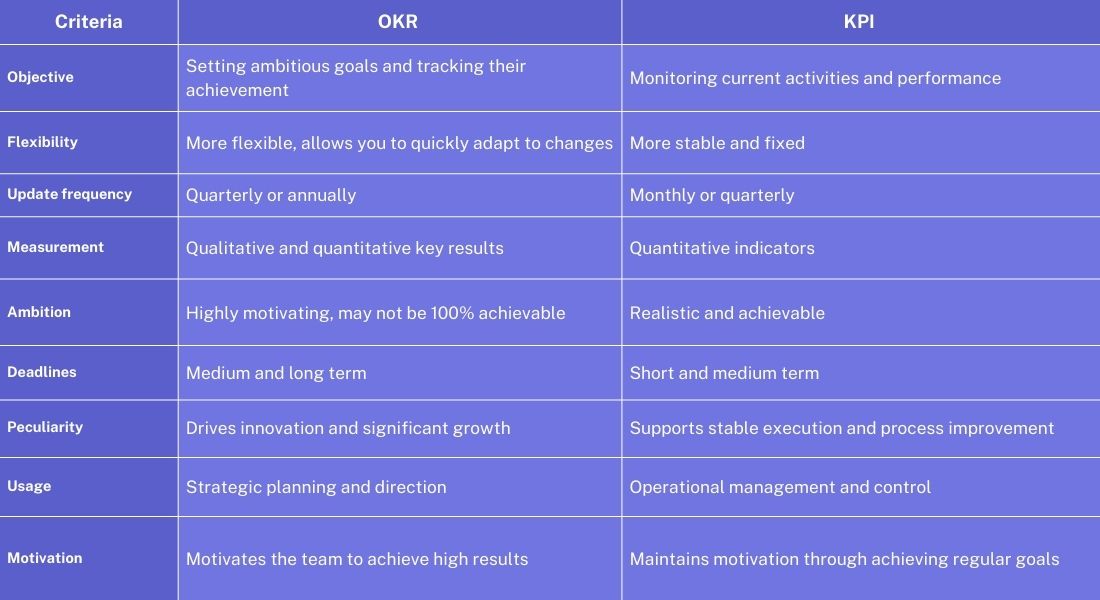
When are OKRs better than KPIs?
When is it better to use OKRs?
- When you need to set inspiring goals that require significant effort and can lead to significant change.
Example: Developing and launching a new product that will change the market or implementing an innovative technology. - When the project aims to explore new opportunities, grow, and innovate.
Example: Implementing a new AI technology or expanding into a new market. - At the start of product development, when goals and deliverables can be revised based on data and feedback.
- When it is important to inspire the team and create a shared vision that guides collective efforts to achieve ambitious goals.
When is it better to use KPIs?
- When you need to track daily operational tasks and ensure stability and control over current processes.
Example: Monitoring server performance, system response time, percentage of successful deployments. - When you need to monitor compliance with security standards, regulations, and internal policies.
Example: GDPR compliance level, number of vulnerabilities identified and fixed. - To evaluate the economic efficiency of a project or processes in order to optimize costs and increase return on investment.
Example: ROI, TCO, operating costs.
How to choose metrics for IT projects?
- Clearly formulate what you want to achieve. Divide goals into strategic and tactical.
- Identify key areas of the project that need to be monitored (quality, productivity, user satisfaction, deadlines, budget, etc.).
- For each key area, determine which quantitative indicators will signal success or problems.
- Choose metrics for which you can collect accurate and relevant data. Check if you have the tools to collect and analyze this data.
- Avoid overload. Focus on the most meaningful indicators.
- Consider the specifics of your project and team. Metrics should be tailored to specific conditions.
- Metrics should be interconnected and provide a holistic view of the project’s progress.
How to motivate your team to use and achieve the set metrics?
First, it is important to clearly explain the meaning and purpose of KPIs. People need to understand why these metrics are important and how they affect the overall success of the company or project. For example, you can hold a meeting where you clearly present the idea of implementing metrics on the project.
Second, make sure that the KPIs are realistic and achievable. Unrealistic or too difficult goals can demotivate the team. When setting metrics, consider the current level of productivity and the capabilities of employees. Set ambitious but achievable goals so that employees feel confident and can see progress.
The third important aspect is recognition and reward. When employees reach or exceed the set KPIs, their efforts should be noticed and encouraged. These can be both tangible rewards (bonuses, premiums) and intangible ones (public recognition, additional days off, opportunities for professional growth). It is important that the rewards are fair and correspond to the contribution of each team member.
Regular reports and reviews will help the team see how far they are going towards their goals. This can be in the form of weekly or monthly meetings where results, problems and achievements are discussed. Visualising progress, for example through graphs or tables, can also significantly increase motivation.
Encourage employees to share their opinions and suggestions regarding KPIs. They may suggest more effective ways to achieve goals or point out problems that are hindering progress.